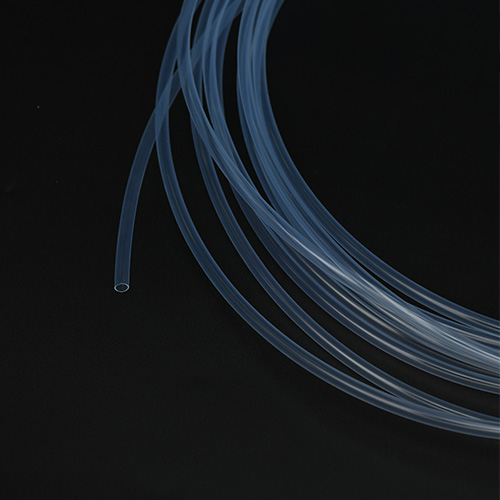
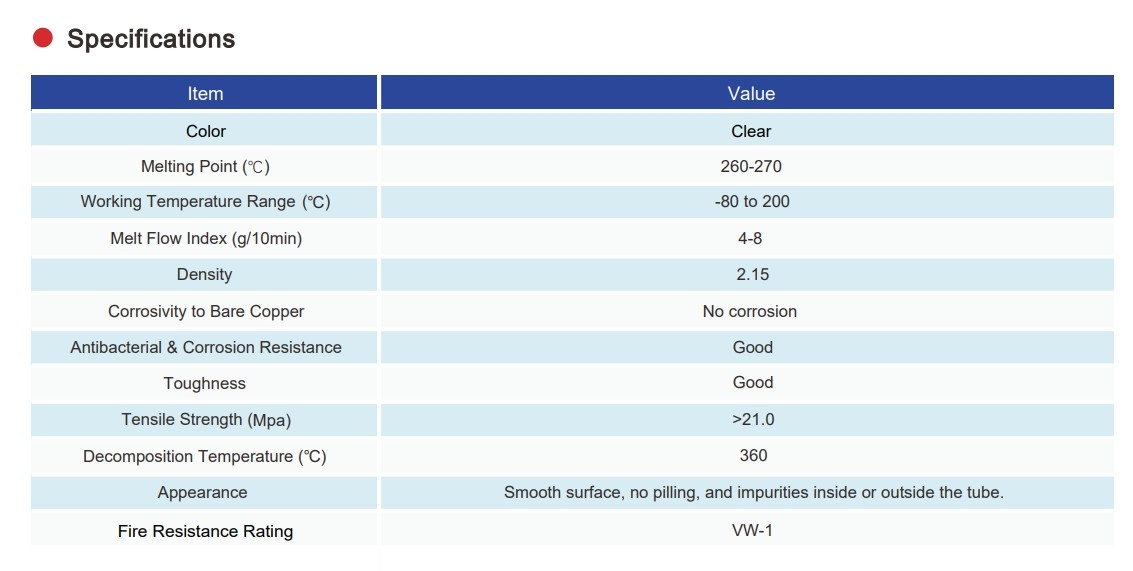




FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) Tubing
FEP/PFA TUBING are two types of high performance plastic tubing.FEP Tubing is processed from fluorinated ethylene propylene copolymers and has excellent resistance to chemical attack, is virtually non-reactive with all chemicals, and possesses good electrical insulation and a low dielectric constant. It is stable over a wide range of temperatures, flexible and easy to bend and mold. PFA Tubing, on the other hand, is made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resin, which has excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, aging resistance and insulating properties. It has a wide range of operating temperatures, and its mechanical strength and chemical stability remain excellent at high temperatures. These two types of tubing have a wide range of applications in the chemical, pharmaceutical, food and electronic equipment fields.

Material Introduction
FEP, or Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene, is a thermoplastic resin formed by the copolymerization of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) and hexafluoropropylene (HFP). It combines the advantages of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) with the processability of thermoplastic materials. Due to its molecular structure containing fluorine atoms, FEP maintains excellent chemical inertness.
Material Properties
Temperature Resistance: FEP retains its physical properties across a temperature range of -200°C to 200°C and can withstand short-term high-temperature shocks.
Chemical Resistance: FEP is unreactive to most chemicals, with some exceptions under extreme conditions such as with alkali metals and fluorine gas.
Insulation Performance: FEP exhibits exceptional electrical insulating properties, particularly important in electrical applications, especially at high frequencies.
Non-Stick Nature: The surface of FEP is extremely smooth, and its non-adhesive qualities mean that almost no substances can form permanent bonds with it.
Transparency: The high transparency of FEP makes it especially popular for applications that require visual inspection of fluid flow.
Product Characteristics
Corrosion Resistance: FEP tubing can withstand the prolonged erosion of corrosive substances without cracking or becoming brittle.
UV Resistance: It does not undergo significant degradation even after prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light.
Gas and Vapor Barrier: FEP material acts as an excellent barrier against gases and water vapor, making it ideal for applications requiring a sealed protective environment.
 Product Advantages
Product Advantages
Thermal Stability: FEP tubing maintains its performance under thermal cycling and heat shock conditions.
Mechanical Strength: While FEP is not as hard as PFA, its flexibility allows for easier installation and use.
Biocompatibility: FEP material complies with FDA regulations, making it suitable for food contact and medical applications.
Application Fields
Chemical: FEP tubing is used in chemical production lines for the transport of corrosive liquids and gases.
Electronics: As a reliable insulator in high-frequency cable production and printed circuit board manufacturing.
Medical: Within the internal tubing of medical equipment and devices that require high-level sterile conditions.
Laboratory: In various instruments within laboratories for connecting and conveying different chemical reagents.
 Material Introduction
Material Introduction
PFA, or Perfluoroalkoxy Alkane, is a fluoropolymer like FEP but with superior thermal stability and moldability, allowing for continuous use at higher temperatures, with a melting point reaching 310°C. Its molecular structure contains alkoxy groups, providing PFA with certain superior properties over FEP.
High-Temperature Endurance: PFA can operate within a temperature range of -200°C to 260°C and withstand higher temperatures for short periods.
Chemical Resistance: PFA exhibits even greater chemical inertness than FEP, especially at elevated temperatures.
Mechanical Performance: PFA has higher compressive strength and hardness, suitable for high-pressure environments.
Purity: PFA has extremely low outgassing, making it suitable for applications such as semiconductor manufacturing that demand extreme cleanliness.
Product Characteristics
Weather Resistance: PFA exhibits outstanding weather resistance in extreme environments.
Creep Resistance: Under long-term high load use, PFA tubing is resistant to creep deformation.
Transparency: Although slightly less transparent than FEP, PFA still allows for sufficient observation of fluid status for applicable uses.
 Product Advantages
Product Advantages
Temperature Resistance: The thermal resistance of PFA makes it particularly suitable for situations requiring high-temperature steam or hot water sterilization.
Chemical Corrosion Resistance: Capable of resisting virtually all chemical corrosions.
Maintenance Cost: Despite the higher initial cost of PFA, its long-term durability may reduce the frequency of replacements, thereby lowering maintenance costs.
Application Fields
Semiconductor Manufacturing: For transporting ultra-pure water and specialized chemicals and use in cleanroom environments.
Chemical: For applications involving higher temperatures, higher pressures, or more demanding chemical conditions.
Aerospace: Utilizing its high-temperature resistance and chemical stability for insulation and sealing materials in spacecraft components.
Biotechnology: In bioreactors and analytical equipment where high cleanliness and contamination resistance are required.
Similarities
- Both materials belong to the fluoropolymer family, meaning they share exceptional chemical stability and electrical insulation capabilities.
- They both exhibit good transparency, suitable for applications that necessitate internal fluid state observation.
- Their non-stick property makes them highly suitable for systems requiring frequent cleaning.
Differences
- PFA surpasses FEP in temperature resistance and mechanical properties, which is also reflected in its cost.
- PFA has a higher processing cost, thus making the market price of the product relatively higher.
- FEP's flexibility makes it more suitable for situations that require bending of the tubing.
- PFA's high purity characteristics make it particularly suited to the semiconductor and aerospace industries.
Our FEP/PFA complies with RoHS, REACH, and FDA requirements.
Our FEP/PFA meets the VW-1 flame resistance rating.
In semiconductor manufacturing, precise fluid transfer is crucial. FEP/PFA Tubing's properties, such as its low friction coefficient and chemical resistance, contribute to maintaining the purity of fluids and avoiding contamination. Exploring these aspects sheds light on the tubing's role in semiconductor applications.
FEP/PFA Tubing is known for its resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for handling corrosive substances in chemical processing. Understanding how FEP/PFA Tubing withstands chemical exposure is essential for industries dealing with aggressive chemicals.
FEP/PFA Tubing is designed to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications where exposure to elevated temperatures is a concern. Exploring the thermal stability and temperature range of FEP/PFA Tubing provides insights into its performance under varying temperature conditions.
In medical applications, FEP/PFA Tubing is chosen for its biocompatibility and clarity. Understanding the specific requirements of medical applications, including sterilization methods and compliance with regulatory standards, is essential for selecting and using FEP/PFA Tubing in the medical field.
Custom sizes and specifications beyond the list are available on request.
The standard color is transparent, and other colors can be customized.
Inner diameters from Φ1 to Φ50 are customizable, with the minimum wall thickness of 0.2mm or more.
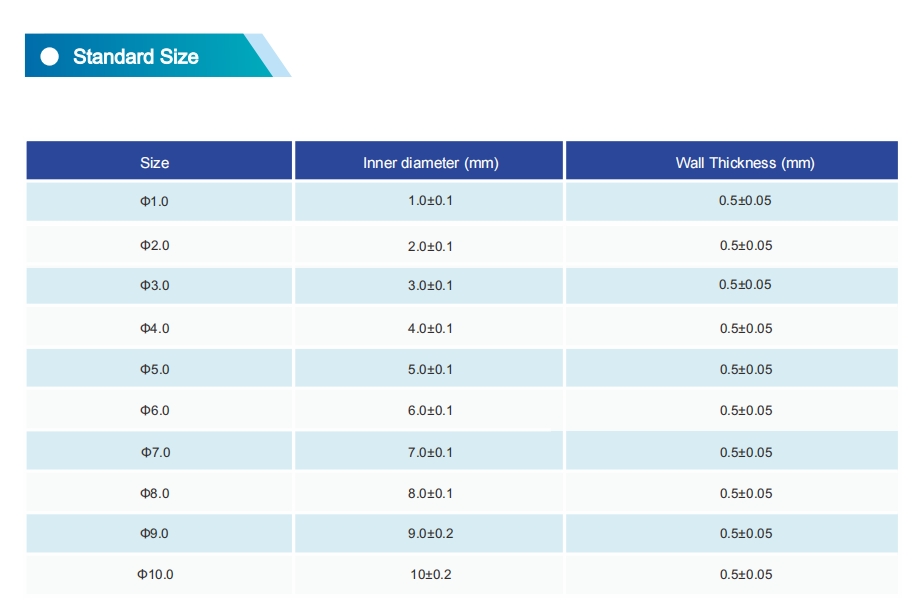
Custom sizes and specifications beyond the list are available on request.
The standard color is transparent, and other colors can be customized.
Inner diameters from Φ1 to Φ50 are customizable, with the minimum wall thickness of 0.2mm or more.