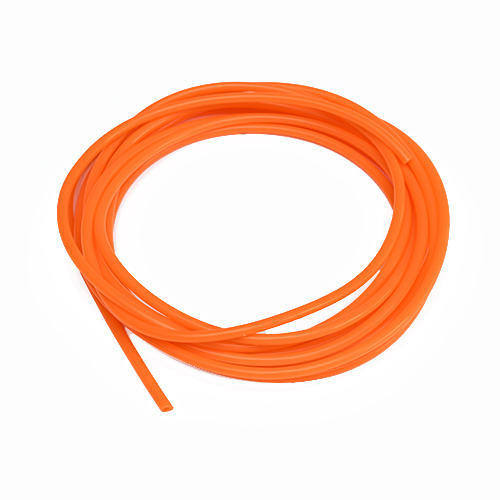
Silicone Rubber Tubing is a critical component in various industries, known for its exceptional flexibility, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures and environmental conditions. From medical devices to automotive systems, food processing, and industrial applications, silicone rubber tubing plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of countless products and processes. The journey from concept to creation of high-quality silicone rubber tubing involves meticulous planning, precise engineering, and stringent quality control measures. This article delves into the comprehensive manufacturing process that transforms raw silicone material into versatile and reliable tubing, ready to meet the demanding needs of diverse industries.
Conceptualization and Design
The manufacturing process of high-quality silicone rubber tubing begins with a clear understanding of the specific requirements and applications for which the tubing is intended. The conceptualization phase involves close collaboration between product designers, engineers, and industry experts to determine the ideal characteristics of the tubing, such as size, shape, flexibility, and material properties. This phase is crucial because the design and material specifications will dictate the performance and suitability of the tubing for its intended application.
Key factors considered during the conceptualization phase include the operating environment, temperature range, pressure requirements, chemical exposure, and any industry-specific regulations or standards that must be met. For example, tubing used in medical applications must comply with stringent biocompatibility standards, while tubing for food and beverage processing must meet FDA or food-grade requirements. Understanding these parameters helps ensure that the final product will perform reliably and safely in its intended environment.
Once the requirements are defined, detailed designs and technical drawings are created. These documents serve as the blueprint for the subsequent stages of manufacturing, guiding the production process and ensuring that the final product meets all specifications.
Material Selection
The choice of material is a critical step in the manufacturing process of silicone rubber tubing. Silicone rubber is selected for its unique combination of properties, including high flexibility, resistance to extreme temperatures, excellent electrical insulation, and biocompatibility. Depending on the intended application, the silicone material may be customized with specific additives or modifications to enhance its performance.
For instance, high-temperature-resistant silicone may be required for tubing used in automotive engines, while medical-grade silicone is necessary for applications involving direct contact with human tissue. The selected silicone material is typically supplied in the form of solid rubber, liquid silicone rubber (LSR), or silicone elastomer, each with distinct processing methods and characteristics.
In addition to the base silicone material, other ingredients such as curing agents, colorants, and reinforcing fillers may be added to achieve the desired properties. These additives are carefully selected to ensure that they do not compromise the performance or safety of the final product.
Extrusion Process
Extrusion is the primary method used to manufacture silicone rubber tubing. This process involves feeding the silicone material through an extruder, a machine that forces the material through a specially designed die to shape it into a continuous tube. The extrusion process is highly versatile, allowing for the production of tubing in various sizes, shapes, and wall thicknesses.
Material Preparation: Before extrusion, the silicone material is thoroughly mixed with any necessary additives to achieve a uniform consistency. The material is then preheated to the appropriate temperature to make it more pliable for extrusion.
Extrusion: The preheated silicone material is fed into the extruder, where it is pushed through a screw or plunger mechanism. As the material moves through the extruder, it is forced through the die, which shapes it into the desired tube form. The die can be customized to produce tubing with specific dimensions, wall thicknesses, and internal or external features, such as ridges or flanges.
Curing: Once the tubing is extruded, it undergoes a curing process to set the shape and solidify the material. Curing can be accomplished through various methods, such as heat curing, where the tubing is exposed to elevated temperatures in an oven, or through the use of curing agents that cause the material to harden at room temperature. The curing process is critical to ensuring the mechanical strength and flexibility of the final product.
Post-Processing: After curing, the tubing may undergo additional post-processing steps, such as cutting to length, trimming, or surface finishing. These steps help achieve the final dimensions and appearance of the tubing, as well as remove any imperfections or excess material.
Quality Control and Testing
Quality control is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each batch of silicone rubber tubing meets the required specifications and standards. Throughout the production process, various tests and inspections are conducted to verify the quality and consistency of the tubing.
Dimensional Accuracy: The tubing is measured to ensure that it meets the specified dimensions, including outer diameter, inner diameter, and wall thickness. Precision is critical, especially for applications where the tubing must fit tightly with other components or where precise fluid flow is required.
Tensile Strength and Flexibility: Tests are conducted to assess the tensile strength and flexibility of the tubing, ensuring that it can withstand the mechanical stresses it will encounter in use. The tubing must be strong enough to resist tearing or deformation while maintaining the flexibility needed for its application.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance: The tubing is subjected to temperature cycling and environmental exposure tests to evaluate its performance under extreme conditions. This is particularly important for tubing used in harsh environments, such as automotive engines or industrial machinery.
Chemical Compatibility: For applications involving exposure to chemicals, the tubing is tested for resistance to various substances, such as oils, solvents, or cleaning agents. This ensures that the tubing will not degrade or become compromised when in contact with specific chemicals.
Biocompatibility: For medical-grade silicone tubing, rigorous biocompatibility testing is conducted to ensure that the material is safe for use in medical devices or for direct contact with human tissue. These tests may include cytotoxicity, sensitization, and irritation studies.
Visual Inspection: A final visual inspection is conducted to identify any surface defects, discoloration, or other imperfections that could affect the appearance or performance of the tubing.
Customization and Finalization
One of the key advantages of silicone rubber tubing is its ability to be customized to meet specific requirements. Customization options include varying the tubing’s color, transparency, and surface texture, as well as adding features such as printing or embossing. These customizations are often tailored to the needs of specific industries or applications.
For example, in the medical field, clear or translucent tubing may be required for easy monitoring of fluid flow, while color-coded tubing can help differentiate between different lines in a complex system. In industrial applications, textured surfaces may be added to improve grip or prevent kinking.
Once the customization is complete, the tubing is packaged and labeled according to the customer’s specifications. Packaging is designed to protect the tubing during transport and storage, ensuring that it arrives in pristine condition and ready for use.
Applications and Industry Impact
The final product, high-quality silicone rubber tubing, is ready for a wide range of applications across various industries. Its versatility, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions make it a preferred choice for many critical applications.
In the medical industry, silicone rubber tubing is used in devices such as catheters, IV lines, and respiratory equipment, where its biocompatibility and flexibility are essential. In the automotive industry, it is used in fuel lines, coolant systems, and seals, where its resistance to heat and chemicals ensures reliable performance. The food and beverage industry relies on silicone rubber tubing for safe and hygienic fluid transfer, while the electronics industry uses it for insulation and protection of wires and cables.
The impact of high-quality silicone rubber tubing on these industries is significant, as it enables the development of products and systems that are safer, more efficient, and more reliable. The ability to customize the tubing further enhances its value, allowing manufacturers to meet the specific needs of their customers and create innovative solutions.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of high-quality silicone rubber tubing is a complex and meticulous journey that begins with conceptualization and ends with a versatile and reliable product. Each step of the process, from material selection and extrusion to quality control and customization, is carefully managed to ensure that the final tubing meets the highest standards of performance and safety. The result is a product that plays a critical role in a wide range of industries, supporting the development of innovative technologies and solutions. As demand for silicone rubber tubing continues to grow, advancements in manufacturing techniques and materials will further enhance its capabilities, solidifying its position as an essential component in modern industry.