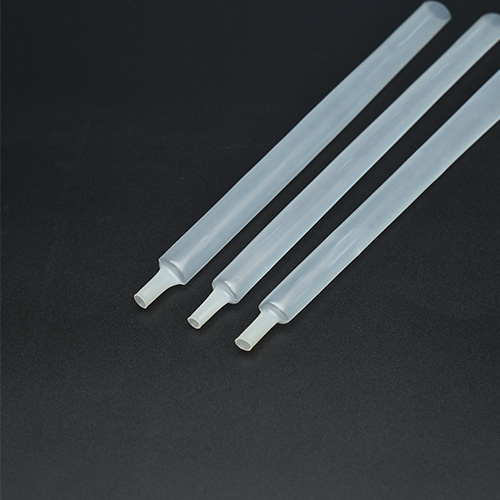
Polyvinylidene fluoride heat shrink (PVDF Heat Shrink) has become increasingly popular in various industries due to its excellent thermal resistance and chemical resilience. Particularly in high-temperature environments, PVDF Heat Shrink demonstrates outstanding performance, providing reliable protection for cables and pipelines. This material not only withstands extreme temperatures but also resists chemical and mechanical damage, making it an ideal choice for sectors such as aerospace, automotive, chemical, and electronics industries.

1. Material Properties of PVDF Heat Shrink
PVDF, or polyvinylidene fluoride, is a semi-crystalline polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and high-temperature performance. PVDF heat shrink typically has superior electrical insulation properties and can operate in temperatures as high as 175°C while maintaining flexibility even at very low temperatures. The standard shrink ratio for PVDF heat shrink is usually 2:1 or 4:1, meaning it can shrink to half or a quarter of its original diameter, providing optimal protection for cables, wires, or pipes in complex applications.
One of the critical properties of PVDF heat shrink is its resistance to UV radiation. Unlike many other plastics that degrade when exposed to ultraviolet light, PVDF remains stable, making it an excellent choice for outdoor applications where prolonged exposure to sunlight is inevitable. Additionally, PVDF heat shrink is highly fire-resistant and self-extinguishing when exposed to flames, significantly reducing the risk of fire hazards.
2. Advantages in High-Temperature Environments
The most notable advantage of PVDF heat shrink is its stability in high-temperature conditions. Many materials lose mechanical strength or insulation properties under extreme heat, but PVDF heat shrink can maintain its integrity and insulation capabilities in temperatures up to 175°C. This feature is particularly critical for industries like aerospace, oil and gas, chemicals, and automotive, where components are exposed to significant temperature fluctuations.
In these industries, equipment and systems must operate continuously in high-temperature environments, subjecting cables and pipelines to harsh conditions. PVDF heat shrink not only tolerates these temperatures but also resists the corrosive effects of acids, bases, oils, and other harmful substances that can develop in high-heat environments, ensuring long-term protection for vital system components.
2.1 Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry demands materials that can function reliably in extreme conditions. Aircraft experience dramatic temperature changes during high-altitude flights, and the internal systems generate heat, further raising the operating temperatures. PVDF heat shrink, with its excellent thermal resistance, protects the electrical systems and wiring in these critical environments, preventing damage due to heat or chemical exposure.
For instance, wiring in aerospace systems needs to be safeguarded against the intense heat generated by onboard systems. PVDF heat shrink can serve as a protective sleeve for these wires, ensuring they remain insulated and functional despite the high operating temperatures.
2.2 Automotive Applications
In modern vehicles, particularly electric vehicles (EVs), the electrical wiring and cabling systems must handle higher operating temperatures than in traditional combustion-engine cars. Batteries, electric motors, and other electronic components generate substantial heat during operation, posing a safety risk if the cables are not adequately protected. PVDF heat shrink provides superior thermal insulation for these essential components, extending the life of automotive cables and improving overall vehicle safety in high-temperature environments.
Additionally, PVDF heat shrink can shield automotive components from exposure to oils, fluids, and corrosive chemicals often found in engine compartments, further enhancing its usefulness in protecting critical automotive systems.
3. Durability and Resistance to Chemicals
Another important feature of PVDF heat shrink is its chemical resistance. In environments such as chemical plants or refineries, where corrosive substances like acids, alkalis, and solvents are commonplace, protecting sensitive equipment from these chemicals is essential. PVDF heat shrink is highly resistant to these substances, preventing degradation over time and ensuring the longevity of the protected components.
In contrast to other materials, which may weaken or deteriorate when exposed to harsh chemicals, PVDF heat shrink maintains its structural integrity, making it a reliable option for long-term use in chemically aggressive environments.
3.1 Oil and Gas Industry Applications
The oil and gas industry is another sector that benefits from PVDF heat shrink's chemical resistance. Pipelines, electrical systems, and other critical components in oil fields and refineries are constantly exposed to hydrocarbons, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. PVDF heat shrink provides these components with robust protection, minimizing the risk of leaks, corrosion, or system failures due to chemical exposure.
3.2 Electronics Industry Applications
In the electronics industry, PVDF heat shrink is often used to protect delicate wires and connectors from heat, chemicals, and physical damage. The material’s high dielectric strength makes it ideal for insulating electrical components, ensuring optimal performance and safety in high-temperature electronic systems.
4. Comparison with Other Heat Shrink Materials
While there are several types of heat shrink tubing available, PVDF stands out due to its combination of high-temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Common heat shrink materials like polyolefin or PVC may offer lower cost options, but they lack the same level of heat and chemical resistance. In environments where these factors are critical, PVDF heat shrink offers superior protection.
For example, in environments where cables or wires are exposed to high temperatures and corrosive chemicals, polyolefin heat shrink may degrade quickly, necessitating frequent replacements. PVDF, on the other hand, will maintain its protective qualities, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring system reliability.
5. Future Trends in PVDF Heat Shrink Applications
With the increasing demand for materials that can withstand harsh environments, the use of PVDF heat shrink is expected to expand into new industries and applications. Emerging sectors like renewable energy, where equipment is often exposed to extreme conditions, will likely benefit from the superior performance of PVDF heat shrink.
In the renewable energy industry, for example, PVDF heat shrink can be used to protect electrical systems in wind turbines or solar power installations. These systems are often exposed to the elements, including UV radiation and temperature extremes, making PVDF an ideal solution for long-term protection.
6. Conclusion
PVDF Heat Shrink’s outstanding performance in high-temperature environments, combined with its excellent chemical resistance and mechanical durability, makes it an indispensable solution for industries where safety, longevity, and reliability are paramount. From aerospace and automotive to oil and gas and electronics, PVDF heat shrink provides critical protection that enhances operational efficiency, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures the safe and reliable functioning of systems exposed to extreme conditions.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of technology, the demand for materials like PVDF Heat Shrink, capable of withstanding the harshest conditions, will only grow, solidifying its place as a vital component in high-performance applications.